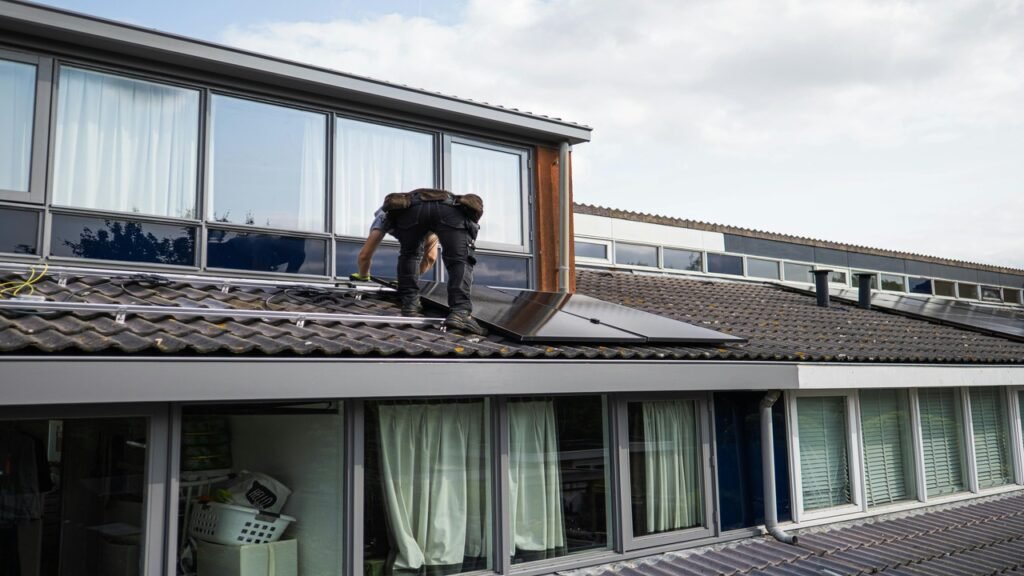
The world is facing a serious energy challenge. Electricity bills are rising, power shortages are becoming common, and extreme weather is pushing people to use more energy at home than ever before.
While many people blame global conflicts and political tensions, the bigger picture shows something more concerning: energy demand is increasing every year, and our traditional energy sources are slowly running out.
Studies from global energy agencies show that worldwide energy consumption continues to rise steadily each year, driven by population growth, urbanization, and increased use of electricity. While the annual increase may appear modest, its cumulative effect over time places significant pressure on energy systems.
Unlike the past, when heavy industries dominated energy use, residential consumption is now growing rapidly. The widespread use of air conditioners, heaters, smart TVs, laptops, electric vehicles, and always-connected devices is significantly increasing the amount of power required by modern homes.
Because of rising costs and environmental concerns, homeowners are now looking for smarter ways to manage and generate energy. Two solutions stand out more than any others: smart homes and solar-powered homes.
Both promise savings, efficiency, and a greener future, but they work in very different ways. Understanding how they compare can help homeowners make better long-term decisions.
Understanding the Energy Crisis and Residential Power Demand
The modern energy crisis is not caused by one single factor. It is a combination of population growth, urbanization, climate change, and increased reliance on electrical devices.
Extreme heat waves and colder winters are pushing households to depend heavily on heating and cooling systems. This has made residential energy use a rapidly growing segment of global electricity demand.
Image credit: Unsplash
Homes today consume energy around the clock. Even when people are asleep, devices like Wi-Fi routers, security cameras, smart assistants, and refrigerators continue to draw power. As more people work remotely and spend time indoors, this consumption keeps increasing.
Governments and environmental experts warn that if residential energy usage continues at this pace, existing power grids will struggle to keep up. This is why energy efficiency and self-generation are no longer optional—they are becoming necessary.
Homeowners now want solutions that can reduce bills without sacrificing comfort. Some prefer smarter energy management through automation, while others want independence by producing their own electricity. This shift has brought smart homes and solar homes into the spotlight.
How Automation Helps Reduce Energy Waste

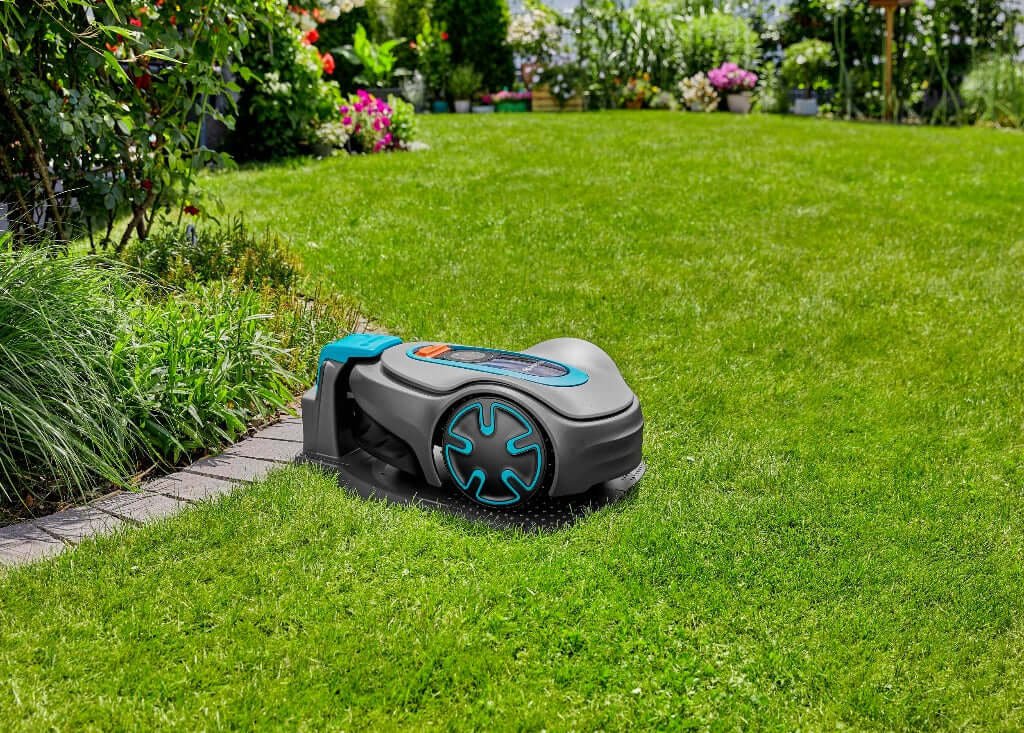
Image credit: Unsplash
A smart home focuses on controlling how energy is used rather than producing it. It relies on internet-connected devices that automate lighting, heating, cooling, security, and appliances. The main goal is to prevent energy waste by making sure power is used only when needed.
For example, smart thermostats learn your daily routine and adjust temperatures automatically. Smart lights turn off when no one is in the room. Smart plugs cut power to devices that would otherwise remain on standby. Over time, these small changes can lead to noticeable savings.
One major advantage of smart homes is affordability. Most smart devices are relatively inexpensive, and homeowners can start small and expand gradually. Installation is usually simple, and many devices work through mobile apps without professional help.
However, smart homes depend heavily on electricity and a stable internet connection. If the power goes out, the automation stops working. Also, while smart homes reduce energy waste, they do not eliminate energy costs entirely. You are still relying on the power grid for electricity.
Smart homes are best suited for urban areas where reliable internet and electricity are available. They offer convenience, better control, and modest energy savings, making them attractive for renters and homeowners who want flexibility.
Producing Clean Energy with Solar Homes
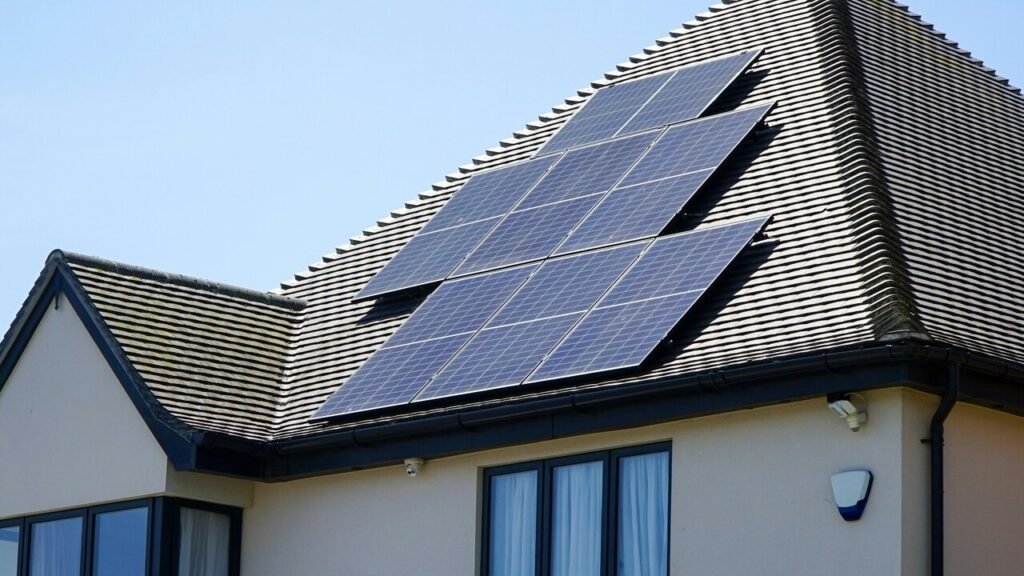

Image credit: Unsplash
Solar homes take a different approach by generating electricity instead of just managing it. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into usable energy, reducing or even eliminating dependence on the grid. This makes solar power one of the most powerful solutions for long-term energy savings.
The biggest benefit of solar homes is cost reduction over time. While installation can be expensive upfront, solar panels can significantly lower monthly electricity bills in many regions. In some areas, homeowners may be able to sell excess power back to the grid through net metering programs, further increasing savings.
Solar homes also offer energy independence. In remote or rural areas where power supply is unreliable, solar systems provide a consistent source of electricity. With battery storage, homes can continue operating even during outages.
Another major advantage is environmental impact. Solar energy is clean, renewable, and produces no emissions during operation. As climate concerns grow, this eco-friendly aspect is driving more people toward solar adoption.
The downside is the initial cost and space requirement. Solar panels need proper sunlight exposure and roof space. Not every home is suitable for installation. Additionally, energy production depends on weather conditions, though modern systems are far more efficient than older ones.
Smart Homes vs Solar Homes
Choosing between smart homes and solar homes depends on budget, location, and long-term goals. Smart homes are cheaper to start with and offer convenience, while solar homes require a higher investment but deliver greater savings over time.
The table below highlights a practical comparison between the two options:
| Feature | Smart Homes | Solar Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low to moderate | High upfront |
| Monthly Energy Savings | 5%–20% | 50%–90% |
| Energy Production | No | Yes |
| Internet Dependency | High | Low |
| Power Outage Support | No | Yes (with batteries) |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate | Very high |
| Best For | Urban homes | Urban and remote homes |
From an environmental perspective, solar homes have a stronger impact because they replace fossil fuel-based electricity entirely. Smart devices help reduce waste, but also create electronic waste due to frequent upgrades and replacements.
Many experts agree that the best solution is not choosing one over the other but combining both. A solar-powered smart home uses clean energy efficiently, maximizing savings and minimizing environmental harm.
Who Smart Homes May Not Be Ideal For
Smart homes are not the best fit for everyone. They may not be ideal for:
- Homeowners in areas with frequent power or internet outages, where automation features may stop working.
- People who prefer simple, manual controls and do not want to rely on mobile apps or cloud services.
- Those concerned about frequent device upgrades, compatibility issues, or electronic waste over time.
Who Solar Homes May Not Be Ideal For
Solar-powered homes also come with limitations and may not suit:
- Homes with limited roof space or poor sunlight exposure due to shading or building orientation.
- Renters or short-term homeowners who may not recover the upfront investment before moving.
- Households in regions without net metering or incentives, where financial payback can take longer.
Hidden Costs People Overlook
When comparing smart homes and solar homes, people often focus only on savings. However, there are other factors to consider:
- Smart homes may require replacing devices over time as technology evolves or platforms change.
- Solar systems may involve maintenance costs, inverter replacements, or battery upgrades after several years.
- Local regulations, permits, and grid policies can affect installation timelines and overall costs.
Final Takeaways
- Both smart homes and solar homes help reduce energy costs, but in different ways.
- Smart homes focus on energy efficiency and automation, while solar homes generate clean power.
- Smart homes are more affordable upfront and ideal for urban lifestyles.
- Solar homes offer long-term savings, energy independence, and strong environmental benefits.
- Internet and grid dependency make smart homes less reliable during outages.
- Solar homes can work even in remote locations when paired with appropriate battery storage.
- The most effective solution is combining solar energy with smart automation.
- A hybrid approach delivers maximum savings, comfort, and sustainability.
As energy demand continues to rise, the future of housing lies in smarter and cleaner solutions. By integrating solar power with smart technology, homeowners can protect themselves from rising costs while contributing to a more sustainable world.


